Virtualization
- Virtualization is the process of creating multiple virtual machines /operating system from one physical hardware box
- Each machine works independently from each other and have their own Operating system
- Each Virtual machine has the Virtual hardware
- Virtual CPU – it is the physical CPU which is allocated to virtual machine
- Virtual storage : it is the pooling of multiple physical storage into a single storage source
- Virtual network: There are two virtual network
- One connect the virtual machine inside the supervisor
- protocol base virtual network like VLAN
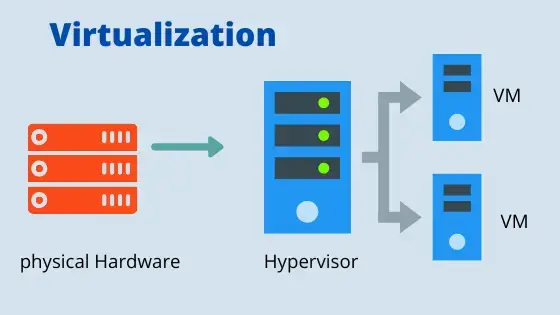
They way it works it's that a software component hypervisor is installed on the physical machine.That hypervisor creates virtual platforms on the physical machine on top of which multiple Operating system are installed and monitored
These virtual platforms are called virtual machine or virtual hardware.Hypervisor is also called Virtual machine monitor.
Guest operating system are then installed on this virtual hardware and the guest OS sees the virtual hardware as if they are its native, actual hardware components.Your apps run on these Guest operating system
Types of Hypervisor
a. Bare metal or Native: In this case, the hypervisor runs directly on the physical machine and creates and monitors the guest operating system. Guest operating runs on the separate layer above the hypervisor.This is called type-1 Hypervisor
For example. 1.-VMware ESX and ESXi 2. Oracle VM: This is based on Open Xen Hypervisor. The virtual machine almost has native performance
b. Hosted hypervisor: In this case, the hypervisor is installed on the host operating system This is called type -2 hypervisor.
For example: A.-. VMware Workstation/Fusion/Player and B.-. Oracle VM VirtualBoxkstation/Fusion/Player
A Virtual Machine (VM) is a compute resource that uses software instead of a physical computer to run programs and deploy apps. One or more virtual “guest” machines run on a physical “host” machine.
Each virtual machine runs its own operating system and functions separately from the other VMs, even when they are all running on the same host. This means that, for example, a virtual MacOS virtual machine can run on a physical PC.
You can have a virtual server, a virtual router or a virtual switch
Containers
Containers are executable units of software in which application code is packaged, along with its libraries and dependencies, in common ways so that it can be run anywhere, whether it be on desktop, traditional IT, or the cloud.
To do this, containers take advantage of a form of operating system (OS) virtualization in which features of the OS are leveraged to both isolate processes and control the amount of CPU, memory, and disk that those processes have access to.
Containers are small, fast, and portable because unlike a virtual machine, containers do not need include a guest OS in every instance and can, instead, simply leverage the features and resources of the host OS.
In a nutshell, containerization is far more efficient than traditional virtualization as it has fewer layers and less complexity.
Container engines can run multiple, isolated instances, known as containers, on the same operating system kernel. Containers perform virtualization at the operating system level, and provide a controllable, easily manageable environment for running applications and dependencies
Maybe you have not a physical machine but a cloud machine with Microsoft Azure or Amazon AWS, but you will need a firewall, a virtual switch, a load balancing in the middle like this
So for that you wil eventually need to create a virtual machine
 Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
August 07, 2022
Rating:
Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
August 07, 2022
Rating:
















No comments: