Enterprise Network Design
Enterprise Network Design
Network enterprises used to use three-tier hierarchical network model for a long time. Cisco suggests Three Layer hierarchical network model, that consists of three different layers for design and deployment purposes, The Core layer, the Distribution layer, and the Access layer.
In this architecture, the core Layer includes the biggest, fastest, and most expensive routers with the highest model numbers and is assumed as the back bone of networks. Core Layer routers are used to merge geographically separated networks in order to move information on the network as fast as possible.
The Distribution Layer which is located in the middle of core and access layers, provide boundary definition by implementing access lists and other filters. So the Distribution Layer defines policy for the network using high-end layer 3 switches and ensures that packets are properly routed between subnets and VLANs in your enterprise.
And finally, Access layer includes access switches which are connected to the end devices such as computers, printers and etc. Access layer switches ensures that packets are delivered to the end devices.
New Spine and Leaf Architecture
In Cisco Spine and Leaf Architecture, every leaf switch is connected to each of the spine switches in a full-mesh topology. The leaf layer includes access switches that connect to devices such as servers while the spine layer is the backbone of the network and is responsible for interconnecting all leaf switches.
The path is randomly chosen so that the traffic load is evenly distributed among the top-tier switches. If one of the top tier switches were to fail, it would only slightly degrade performance throughout the data center.
Cisco Fabric Path Spine-and-Leaf Network
The FabricPath spine-and-leaf network provides a simple, flexible, and stable network, with high scalability and fast convergence characteristics. FabricPath IS-IS as its control plane, is designed to determine FabricPath switch ID reachability information. To know end-host reachability information, FabricPath switches rely on initial data-plane traffic flooding.
A Layer 3 function is laid on top of the Layer 2 network. Common Layer 3 designs use centralized routing: that is, the Layer 3 routing function is centralized on specific switches
Reasons for cloud computing
The cost of acquiring and maintaining hardware is still one of the main reasons why IT activities are outsourced to a service provider that sits outside the company’s own buildings. In addition to the actual acquisition of hardware, having employees who are competent in handling this physical product is also necessary.
Fabric capacity planning
FHRP
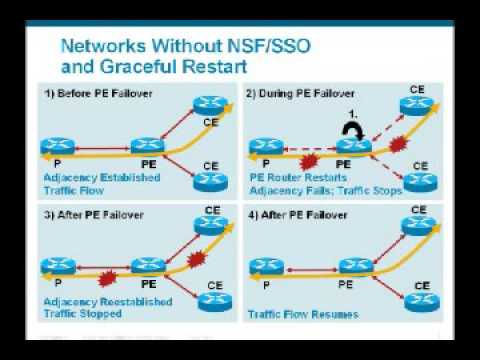
Stateful Switchover (SSO)
Routers designed for high availability (HA) include hardware redundancy such as dual power supplies (PSU) and router processors (RP). The RP is responsible for for learning the network topology and building the route table (RIB).
Stateful Switchover (SSO) is a redundancy feature that allows a Cisco device with two route processors to synchronize router configuration and control plane state information.
The processing of mirroring this information between route processors is known as checkpointing. Stateful Switchover enabled routers will always checkpoint line card operation and Layer 2 protocol states.
Enabling additional configuration in the form of nonstop forwarding (NSF) or nonstop routing (NSR) will keep CEF entries for a short duration in a failover event to keep packet forwarding in an event of an RP failure until the control plane has time to recover.
 Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
August 29, 2022
Rating:
Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
August 29, 2022
Rating:


















No comments: