Software Define Network (SDN)
Software-defined networking (SDN)
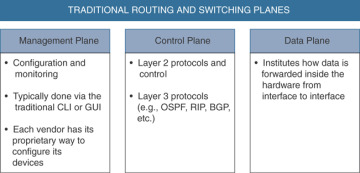
In traditional networking, there are three different “planes” or elements that allow network devices to operate: the management, control, and data planes
The control plane has always been separated from the data plane. There was no central brain (or controller) that controlled the configuration and forwarding.
Software-defined networking (SDN) is an architecture designed to make a network more flexible and easier to manage. SDN centralizes management by abstracting the control plane from the data forwarding function in the discrete networking devices.
- SDN elements
- An SDN architecture delivers a centralized, programmable network and consists of the following:
- A controller, the core element of an SDN architecture, that enables centralized management and control, automation, and policy enforcement across physical and virtual network environments is the software that provides a centralized view of and control over the entire network. Network administrators use the controller how the underlying infrastructure’s forwarding plane should handle the traffic. The controller is also used to enforce policies that dictate network behavior.
- Southbound APIs that relay information between the controller and the individual network devices (such as switches, access points, routers, and firewalls) .The network infrastructure is told what path the application data must take as decided by the controller.
- Northbound APIs that relay information between the controller and the applications and policy engines, to which an SDN looks like a single logical network device
SDN Benefits
SDN offers a centralized, programmable network that can dynamically provision network resources so as to address the changing needs of businesses. It also provides the following technical and business benefits
SDN Challenges
- Security risks of centralized management: While this makes networking easier, it is also a security risk. Centralized management is a single point of attack and if it goes down
- SDN controller bottleneck: When there is only a single instance of an SDN controller, it can become a bottleneck for a network with a large amount of traffic, routers, and switches.
- No universally-accepted standard for northbound APIs: Without a universally-accepted standard for northbound APIs, vendors and open source organizations are making dissimilar APIs for their SDN controllers.
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC)
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller (APIC) is the single point of policy and management of a Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI) fabric.
Cisco APIC re-defines how Cisco networks are managed and operated.
Cisco’s application centric infrastructure (Cisco ACI) is ideally suited for the distributed 5g architecture. ACI network is 5G ready which fundamentally brings the capabilities of centralized provisioning and policy management built-in security with a whitelist for hardware-based encryption, telemetry an intelligent dashboard and an assurance engine that continuously verifies and validates the entire data center network.
Cisco ACI is a policy-driven solution that integrates software and hardware. The hardware for it is based on the Cisco Nexus 9000 family of switches. The software and integration points for ACI include a few components, including Additional Data Center Pod, Data Center Policy Engine, and Non-Directly Attached Virtual and Physical Leaf Switches.
In a leaf-spine ACI fabric, Cisco is provisioning a native Layer 3 IP fabric that supports equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) routing between any two endpoints in the network, but uses overlay protocols, such as virtual extensible local area network (VXLAN) under the covers to allow any workload to exist anywhere in the network. Supporting overlay protocols is what will give the fabric the ability to have machines, either physical or virtual, in the same logical network (Layer 2 domain), even while running Layer 3 routing down to the top of each rack.
SDN changed a few things in the management, control, and data planes. However, the big change was in the control and data planes in software-based switches and routers (including virtual switches inside of hypervisors).
.
Cisco ACI supports VLAN, VXLAN, and network virtualization using generic routing encapsulation (NV-GRE), which can be combined and bridged together to create a logical network/domain as needed.
In traditional Cisco networks, each node is managed independently, via the command-line interface (CLI), which is time-consuming, tedious, and error-prone.
In ACI networks, network admins use the APIC to manage the network – they no longer need to access the CLI on every node to configure or provision network resources.
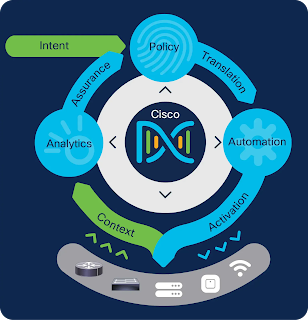
Cisco DNA
Cisco DNA objective is to us to automate workflows and deployments across disparate systems in order to streamline operations across domains. Automation has a number of advantages.
Cisco DNA Center is based on something called Intent-Based Networking, a new approach to networking in that the network admin can now define and input what the needs of the network are into the IBN software controller.
This ensures that the network works in conjunction with the needs of the business.
Overlay and underlay network
Overlay networks are virtual logical networks constructed on an underlay network using network virtualization technologies. Although different overlay networks share devices and lines on an underlay network, services on overlay networks are decoupled from physical networking and interconnection technologies on the underlay network.
To get rid of the limitations of underlay networks, virtual overlay networks can be created over underlay networks using network virtualization technologies. For example
An underlay network, as the name implies, is the underlying physical infrastructure of overlay networks.
This is a traditional Underlay network
The control pane functions are decoupled from the router
The tunnels are not inside the router , the tunnels and configuration are inside the sd-wan controller
Cisco Viptella SD-WAN
 Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
July 11, 2022
Rating:
Reviewed by ohhhvictor
on
July 11, 2022
Rating:





























No comments: